Map Of Chagos Archipelago - 6°00′S 71°30′E / 6.000°S 71.500°E / -6.000; 71.500 Coordinates: 6°00′S 71°30′E / 6.000°S 71.500°E / -6.000; 71,500
Chagos Islands (/ ˈ tʃ ɑː ɡ ə s , -ɡ oʊ s / ) or Chagos Islands (formerly Bassas de Chagas,
Map Of Chagos Archipelago
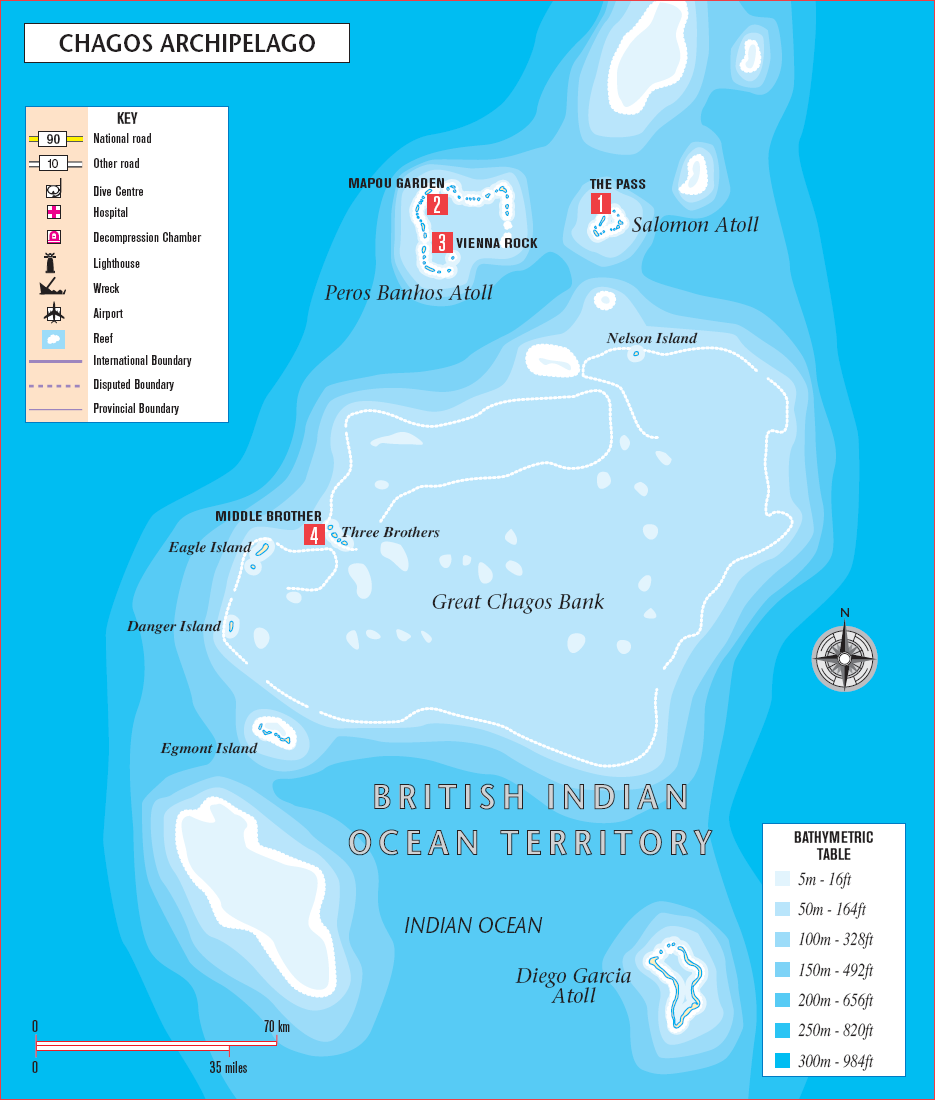
And later the Tel Islands) is a group of contained atolls consisting of more than 60 islands in the Indian Ocean, about 500 kilometers (310 mi) south of the Maldives. This island chain is the southernmost archipelago of the Chagos-Laccadive Ridge, a long submarine mountain range in the Indian Ocean.
File:chagos Archipelago Location Map.svg
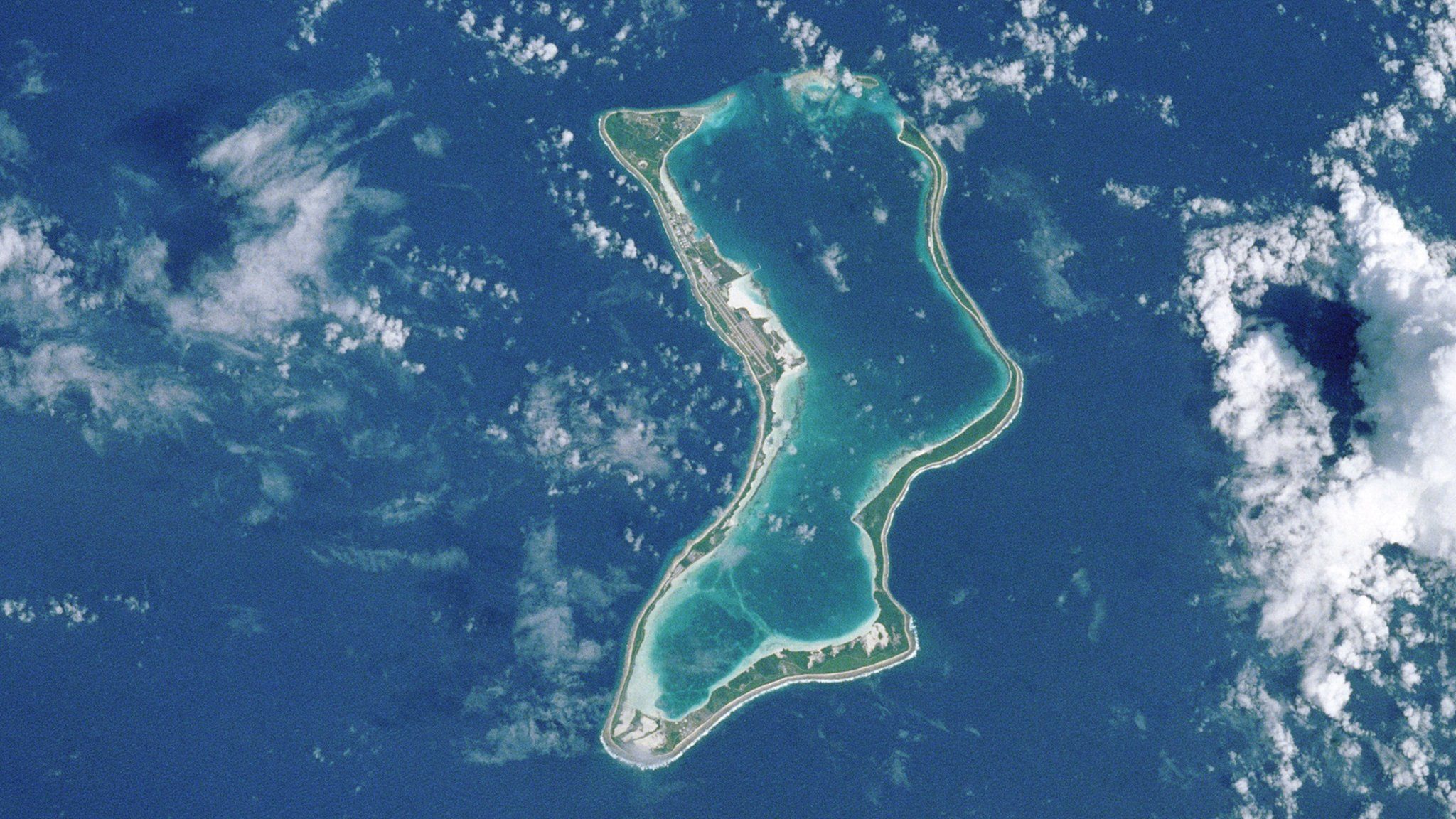
To the north are the Solomon Islands, Nelson Island and Perros Banhos; On its southwest side are Three Brothers, Eagle, Egmont, and Danger Island; To its southeast is Diego Garcia, by far the largest island. All are low atolls, except for a few very small examples, surrounding the lagoon.
The Chagos Islands were home to the native Chagossians, a Creole-speaking Bourbonnais, until the United Kingdom expelled them from the islands at the request of the United States between 1967 and 1973, to allow the United States to build a military base in Diego. Garcia. Since 1971, only the atoll of Diego Garcia has been inhabited, and only by US military personnel, including US civilian contract workers. Since the expulsion, the Chagossians, like all others not authorized by the UK or US governments, have been prevented from destroying the islands.
While Mauritius was a French colony, the islands belonged to the French administration of Mauritius (Île Maurice). With the Treaty of Paris in 1814, France ceded Mauritius and its territories to the United Kingdom.
In 1965, the United Kingdom made the Chagos a British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) while planning to make Mauritius independent.
The Chagos Question
Mauritius gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1968 and has since claimed the Chagos Islands as Mauritian territory.
In 2019, the International Court of Justice (ICJ) issued a non-binding advisory opinion stating that "...the United Kingdom has an obligation to implement the administration of the Chagos Islands as soon as possible and all member states to cooperate with United Nations to complete the decolonization of Mauritius."
In December of that year, Sega Tambour's Gray Chagos was recognized as Intangible Cultural Heritage by UNESCO from Mauritius.

In 2021, the International Tribunal for the Law of the Sea confirmed its jurisdiction that the United Kingdom "has no sovereignty over the Chagos Islands" so the islands must be returned to Mauritius.
Chagos Islands: International Court Of Justice Says U.k. Broke International Law
In August 2021, the Universal Postal Union banned the use of British stamps in BIOT, a move that Mauritian Prime Minister Pravinda Jugnauth called "a major step in favor of recognizing Mauritian sovereignty over the Chago".
Additional references are required to verify this section. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (July 2021) (Learn how and what to remove this template message)
The archipelago is about 500 kilometers (310 mi) south of the Maldives, 1,880 kilometers (1,170 mi) east of the Seychelles, 1,680 kilometers (1,040 mi) northeast of Rodrigues Island, 270 kilometers (1,700 mi) 3,40 west of Cocos (Keeling) Islands and north of Amsterdam Island.
Calculated from the Great Chagos Bank, the largest known atoll structure in the world (the fully submerged Saya de Malha Bank is large, but its status as an atoll is uncertain). The surface of the shelf is 20,607 km
Location Of Study Area And Coral Sample Locations. The Chagos...
, and the Exclusive Economic Zone, which borders the corresponding territory of the Maldives in the north, has an area of 639,611 km.
The Chagos Group is a cluster of coralline rock formations atop a southward-flowing submarine ridge in the Indian Ocean, formed by volcanism above the Réunion hotspot. Unlike the Maldives, there is no clearly discernible pattern in the arrangement of the atoll, which makes the entire archipelago seem somewhat chaotic. Most of the coral structures in the Chagos are submerged reefs.
Chagos has the world's largest coral atoll, the Great Chagos Bank, which supports half of the total area of good quality reefs in the Indian Ocean. As a result, Chago ecosystems have so far proven resilient to climate change and biotic disturbances.
In addition to saving atolls with dry land reaching at least high water mark, there are nine reefs and shores, most of which can be considered permanently submerged atoll structures. The number of atolls in the Chagos Islands is usually four or five, plus two groups of islands and two single islands, mainly because the Great Bank of Chagos is not known to be a large atoll structure (two single islands with these two groups of islands). and because Bloheim Reef, which contains islands or hairs or reaches high water, is not included. The features are listed in the table from north to south:
Un Hands British Chagos Islands To Mauritius
The main natural resources of the area are coconuts and fish. Commercial fishing licenses provide an annual income of around $2 million for the British Indian Ocean Territory Authority. However, licenses have not been issued since October 2010; The deadline for establishing an unclaimed marine reserve has expired.
All economic activity takes place on the larger island of Diego Garcia, home to the joint UK-US military installation. Construction projects and various services required to support military installations are performed by military and contract personnel from the United Kingdom, Mauritius, the Philippines, and the United States. There are no industrial or agricultural activities on the island. All water, food and other items of daily life are shipped to the island. An independent feasibility study concluded that relocation would be "costly and unsafe". Another feasibility study, carried out by organizations supporting relocation, found that relocation would be feasible for the British taxpayer at £25 million. If the Chagossians return, they plan to restore copra production and fishing and begin commercial development of the islands for tourism.
As of October 2010, yellowfin tuna (Euthinus pelamis) and yellowfin tuna (Thunus albacares) were fished for about two months of the year, as their year-round migration route takes them through Chagos waters. Although the remote area of the Chagos offers some protection from extractive activities, legal and illegal fishing has had an impact. Turtles and other marine animals are being hunted to a considerable extent. Sharks, which play an important role in balancing the food web of tropical reefs, are in sharp decline due to illegal fishing for their fins and bycatch in legal fisheries. Sea cucumbers, which scour the sand, are ripened to feed Asian markets
The Chagos Islands have a tropical oceanic climate; Hot and humid, but moderated by trade winds. The climate is characterized by abundant sunshine, warm temperatures, showers and light winds. From December to February is the rainy season (summer monsoon); Typical weather conditions include mild west-northwest winds and warm temperatures with high rainfall. June to September is considered the dry season (winter), characterized by moderate southeasterly winds, slightly cooler temperatures and less rainfall. Average annual rainfall is 2,600 mm (100 in), ranging from 105 mm (4 in) in August to 350 mm (14 in) in January.
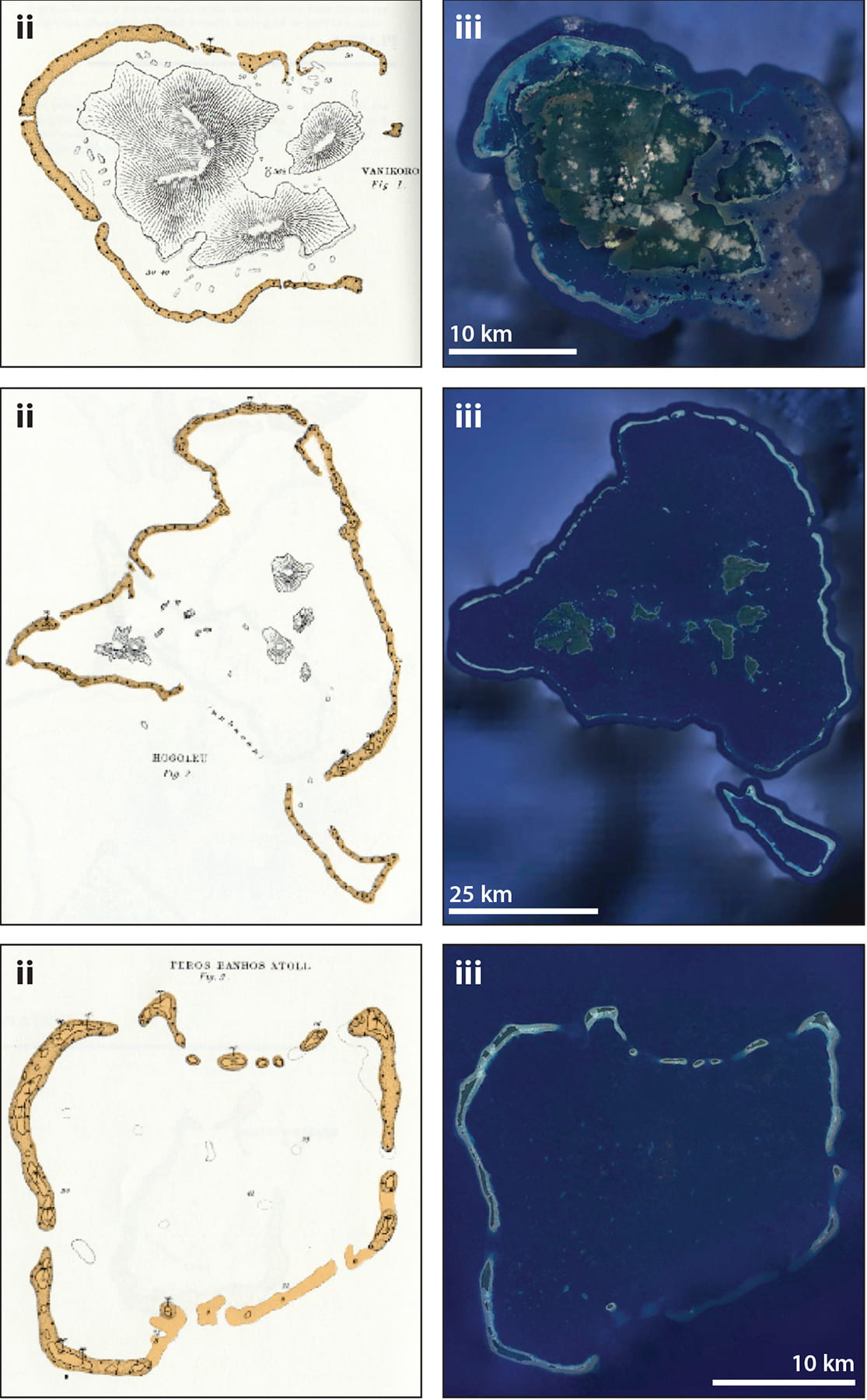
Study: Darwin's Theory About Coral Reef Atoll
According to oral tradition in the southern Maldives, local traders and fishermen were sometimes lost at sea and stranded on an island in the Chagos. By chance, they were rescued and returned to the country.
However, these islands were considered too far from the Maldives to be permanently settled by the Maldivians. Thus for a long time the Chagos were neglected by their northern neighbors.
In Maldivian lore the whole group is known as Folhavahi or Holabhai (surname in the southern Aduan Maldivian dialect of Dhivehi). In Maldivian oral tradition, the various Chagos atolls do not have separate names.

The first Europeans to become aware of the archipelago were Portuguese explorers. Although the Portuguese navigator Pedro de Mascarhas (1470 – 23 June 1555) is credited with having encountered the islands during the 1512–1513 voyage, there is little evidence for this; Cartographic analysis indicates 1532 or later.
India Mauritius Joint Trade Committee
Portuguese: Chagas (wound) refers to the sacred wound of Jesus' crucifixion. They also named several atolls, such as Diego Garcia and Perros Banhos Atoll, named Pedro dos Banhos by Alfonso de Albuquerque in 1513.
Neglected by the Portuguese, this isolated and isolated group, economically and politically disinterested, did not become part of the Portuguese Empire.
Before coconut trees were widely grown on the islands, the earliest and most interesting description of the Chagos was written by Manuel Rangel, from the Portuguese ship Concecio, which ran aground on the Perros Banhos reef in 1556.
Chagos was first claimed by the French after the settlement of Île Bourbon (now Réunion, in 1665) and Île de France (now Mauritius, in 1715). The French began issuing permits to companies to establish coconut oil plantations in the Chagos in the 1770s.
Chagos Islands: Mauritius's Latest Challenge To Uk Shows Row Over Sovereignty Will Not Go Away
The Chagos Islands and Diego Garcia were claimed for Great Britain on 27 April 1786. However, the territory was ceded to Britain by treaty only after the defeat of Napoleon
Birds of indonesian archipelago, map of the azores archipelago, map of indonesian archipelago, chagos archipelago tourism, definition of a archipelago, map of stockholm archipelago, chagos archipelago map, map of archipelago, archipelago of san bernardo, chagos archipelago, map of malay archipelago, chagos islands map
0 Comments